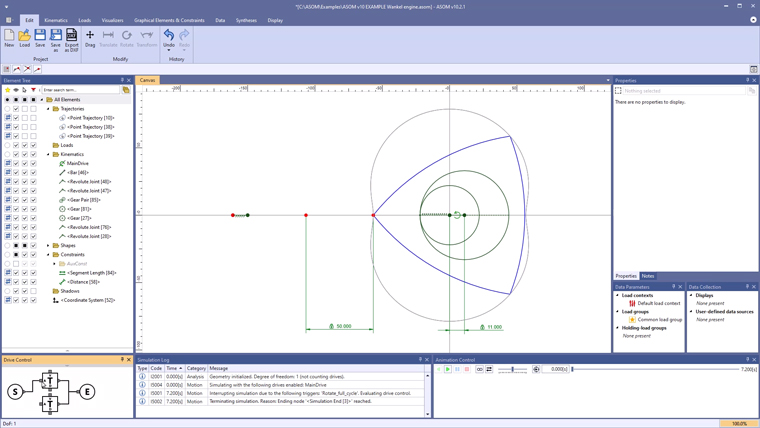
The right table leg has a wheel, while the left one does not. Thus the left table leg corresponds to a sliding bearing (with a sliding friction coefficient of µ=0.6 for wood on stone), while the right table leg corresponds to a rolling friction (with an idealized rolling friction coefficient of µ=0). Depending on the height at which the force to move the table is applied, it could happen that the right table leg would lift off. This can be inferred from the fact that the measured normal force on the right becomes negative.
This website is aimed exclusively at companies and legal entities under public law.
Kinematic and kinetostatic analysis of a table being pushed
This example created with the kinematics software ASOM v7 shows how the normal forces in the two table legs change or adapt when a horizontal force is applied to move the table.

Play Video